Scientific classification
Kingdom:Animalia
Phylum:Nematoda
Class:Secernentea
Order:Tylenchida
Family:Heteroderidae
Genus:Meloidogyne
Species:M. enterolobii
Binomial name:Meloidogyne enterolobii
Introduction
Meloidogyne enterolobii was originally described from a population collected from the pacara earpod tree (Enterolobium contortisiliquum (Vell.) Morong) in China in 1983. In 2001 it was reported for the first time in the continental USA in Florida. M. enterolobii is now considered one of the most important root-knot nematode species because of its ability of reproducing on root-knot nematode-resistant (Mi-1 gene carrying genotypes) bell pepper and other economically important crops.
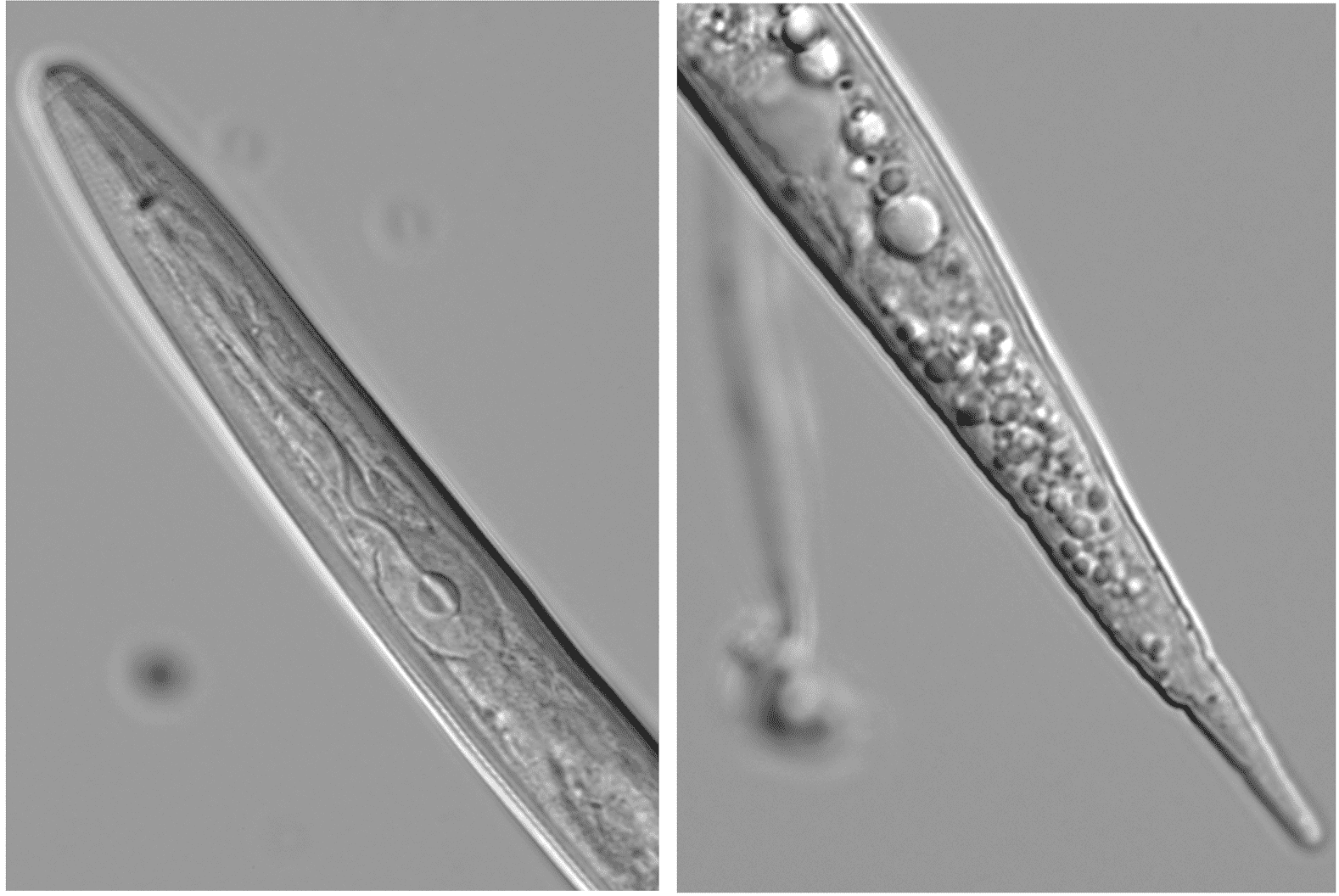
Morphology
M. enterolobii, a sedentary endoparasite, has very similar morphology as other species of Meloidogyne. The perineal patterns, male stylet length values (smaller for M. enterolobii than M. incognita) and J2 tail length values (greater for M. enterolobii than M. incognita) of M. enterolobii isolates from Florida are useful morphological characters for the separation of M. enterolobii from M. incognita. Other methods such as enzyme analyses and DNA analysis also have been performed to identify M. enterolobii from other Meloidogyne species.
Reproduction
M. enterolobii is an apomictic species of root-knot nematodes.
Distribution
M. enterolobii is a tropical or subtropical species reported in Brazil, Venezuela, China, Cuba, France, Guatemala, Puerto Rico, Martinique, Malawi, Senegal, South Africa, Switzerland, Trinidad and Tobago, United States, and West Africa (Ivory Coast and Burkina Faso).
Host
It has a variety of hosts, such as eggplant (Solanum melongena), bell pepper (Capsicum annuum), soybean (Glycine max), sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas), tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum), tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum), watermelon (Citrullus lanatus).
