Scientific classification
Kingdom:Animalia
Phylum:Nematoda
Class:Secernentea
Order:Tylenchida
Family:Heteroderidae
Genus:Meloidogyne
Species:M. javanica
Binomial name:Meloidogyne javanica
Introduction
Meloidogyne javanica is a nematode pathogen that affects over 770 species of plants (Cabi 2018). The hosts of this pathogen include both weeds and crops of economic importance. Those of economic importance include tea, grapevine, vegetables, fruit trees, cereals, and ornamentals (Cabi 2018). Meloidogyne javanica is considered an agricultural pest, as it is extremely abundant and damaging (Alford 2012).
Symptoms
Because there are so many different hosts for this pathogen, the symptoms are very variable. Common symptoms include abnormal leaf color, abnormal leaf form, wilting leaves, galls, swollen roots, reduced root system, dwarfing and senescence (Cabi 2018). This pathogen does the most damage when present in light soils with hot weather conditions (Alford 2012).
Diagnosis
Morphological characteristics
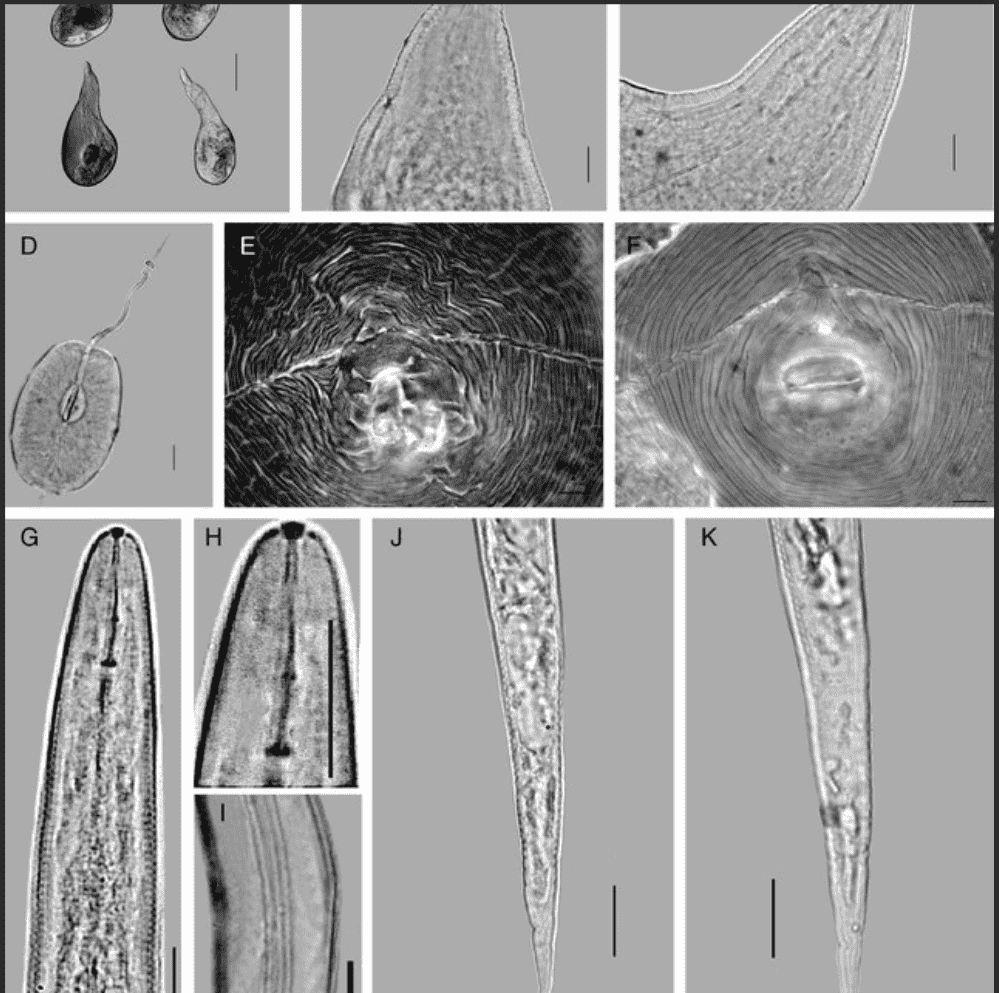
Because there are many plant hosts and variable symptoms, it is important when diagnosing Meloidogyne javanica to obtain a specimen of the nematode from symptomatic plant tissue. The most commonly utilized diagnostic techniques are the use of morphological characteristics of the nematode species (Cunha et al. 2018). Head shape and stylet morphology of males are useful characteristics in the identification of M. javanica. When specimens are placed in the lateral position, the distance between the dorsal esophageal gland orifice to the stylet base can be used to distinguish between species of Meloidogyne (Cunha et al. 2018). In the case of M. javanica, the distance between these two features is relatively short (2.0-3.0 um). Additionally, M. javanica can be diagnosed by looking at the perineal pattern of females. The shape of the perineal region, dorsal arch, dorsal striae, lateral lines and phasmids are all characteristics useful in identification.[citation needed]
Biochemical
Biochemical diagnostic methods are commonly used when diagnosing nematode diseases. One technique frequently utilized is isoenzyme phenotyping (Cunha et al. 2018). Protein extract from M. javanica is applied to a gel electrophoresis to use as a reference phenotype. This analysis is based on the mobility of the enzymes in the extracted protein, which is diagnostic of different species of Meloidogyne (Cunha et al. 2018).
Molecular
There are many molecular techniques that are becoming increasingly more common, as they are easy, quick, and cheap (Cunha et al. 2018). Species-specific PCR is commonly utilized, which uses species-specific primers to target certain nematodes based on SCAR (sequence-characterized amplified region) (Qiu et al. 2006, Cunha et al. 2018). These markers are used for species-specific diagnosis of Meloidogyne (Cunha et al. 2018).
